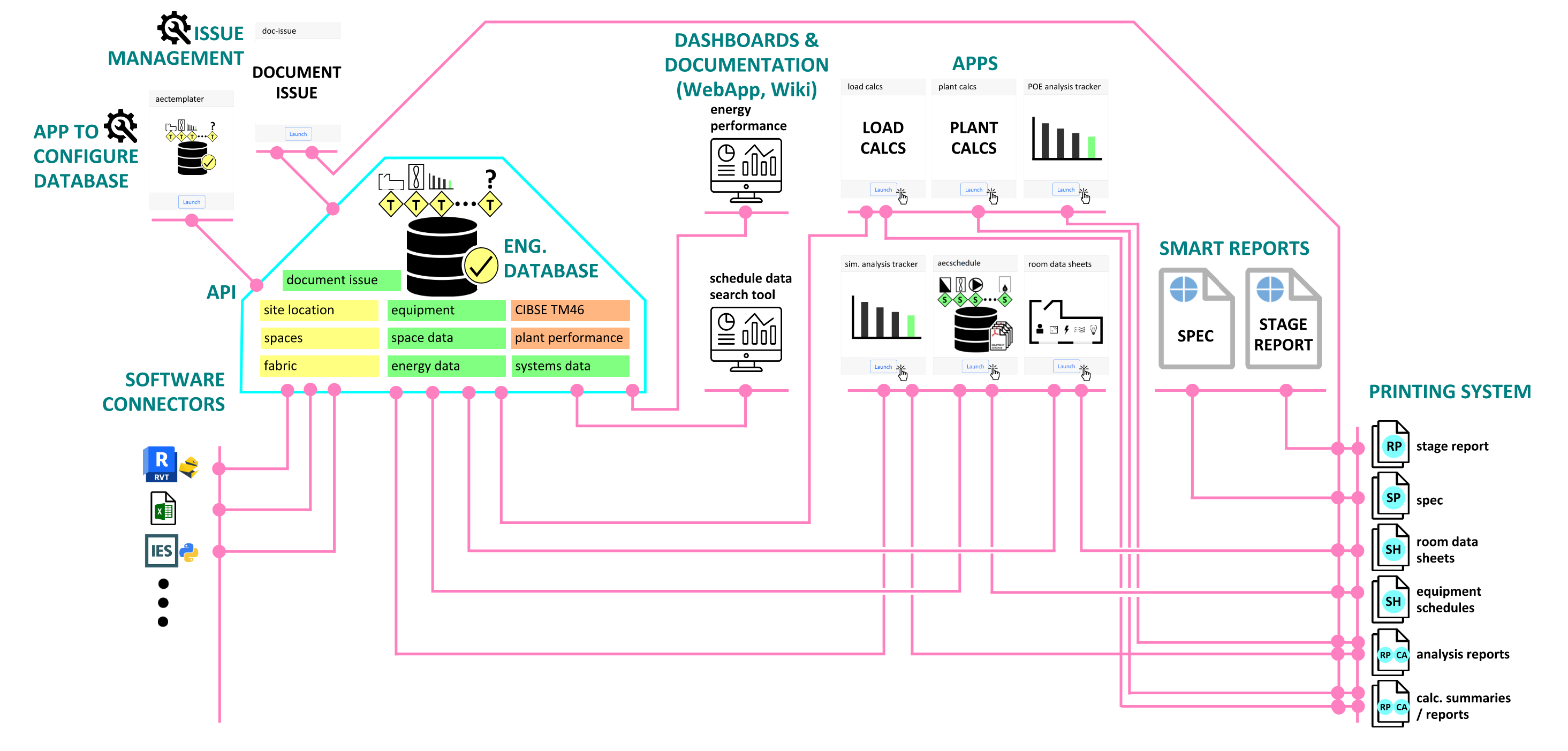
Max Fordham Engineering Development Tech Stack
devops
To enable and facilitate the development of automation tools and applications at Max Fordham required the design and implementation of new tech infrasture. This is described by the image below, and summarised as follows:
- centralised data storage in an SQLite database with a python FastAPI backend
- apps interact with the backend database centrally storing data whilst delivering design automation to the project
- apps are typically built with python and voila
- the centralised engineering data is summarised on dashboards
- dashoards are typically built with javascript and observable framework
- jupyterlab and quarto can be used ad-hoc to query the backend database to create data-driven smart reports. Using
document-issuethese can be issued as formatted pdf documents. - data from user applications like Revit (using pyRevit) or IES (using IES scripting interface) can be pushed and pulled from the database
- the servers are deployed and configured using ansible
- all apps and packages are built on Github. pixi is used for package configuration. Github CI is used for testing and building docs
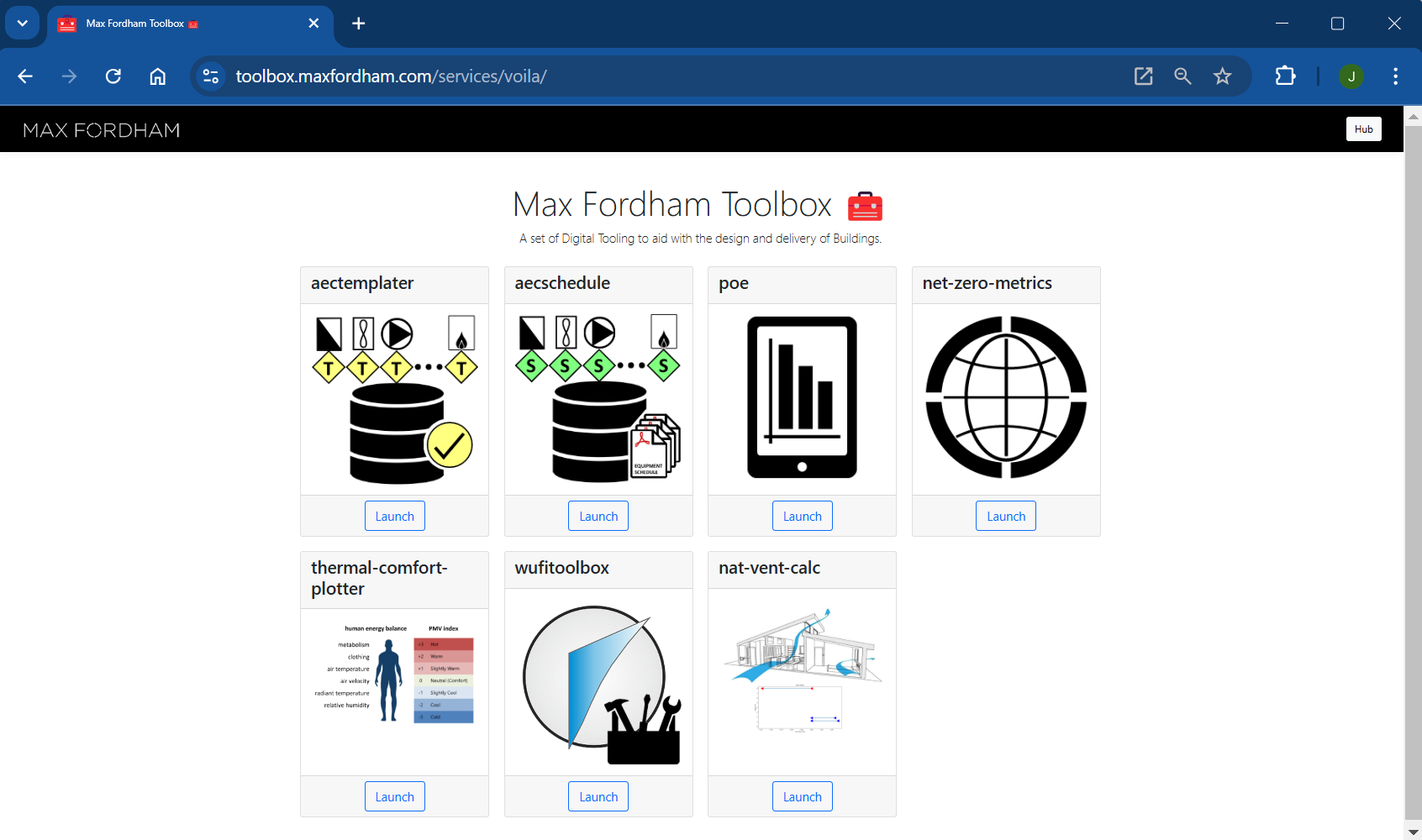
Toolbox
The user-facing app store is a (tljh-voila-gallery)[https://github.com/voila-dashboards/tljh-voila-gallery]:
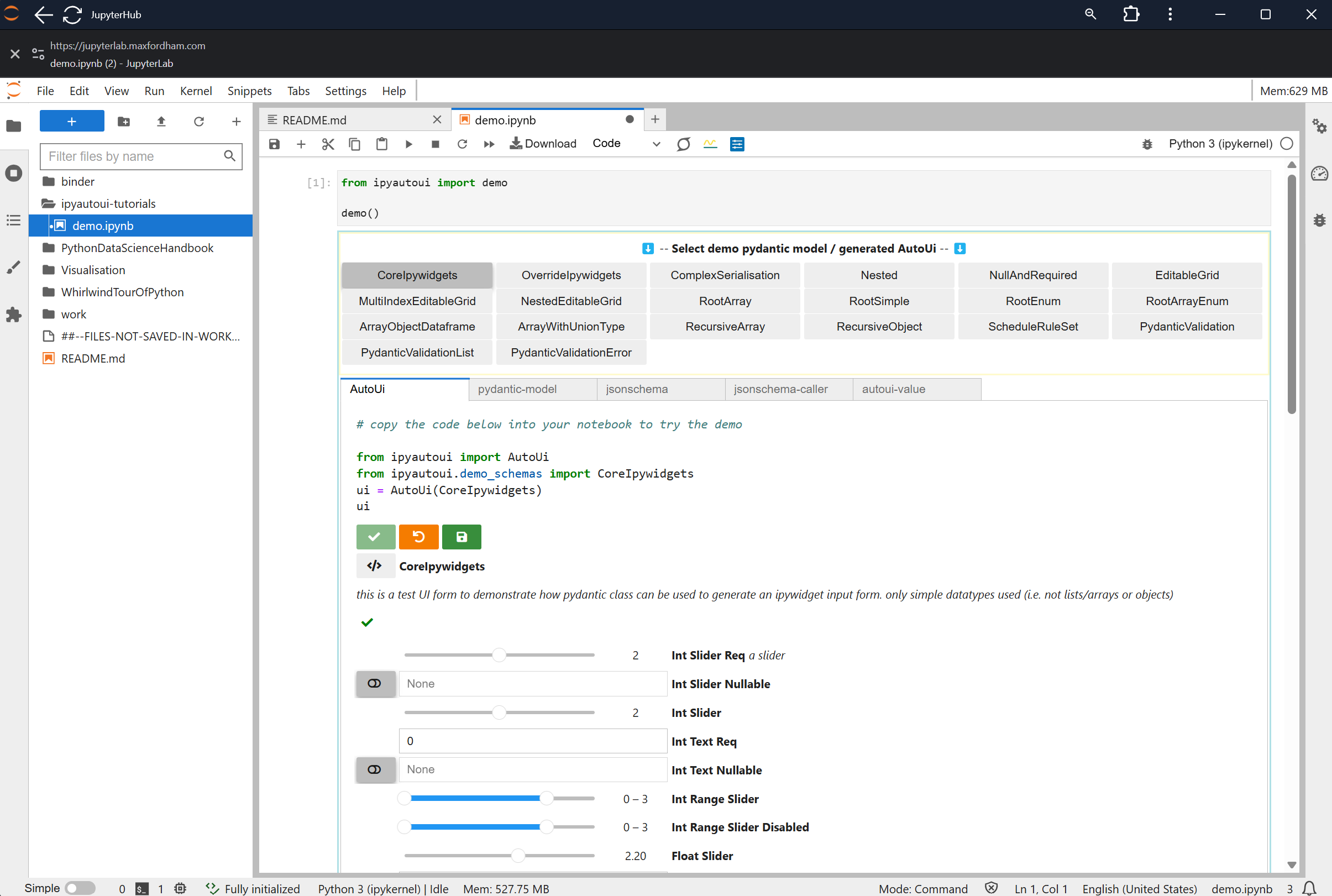
JupyterLab
Engineers are also given access to an internal jupyterlab configured with Max Fordham standard tools, enabling them to interact with engineering data stored in the backend database.
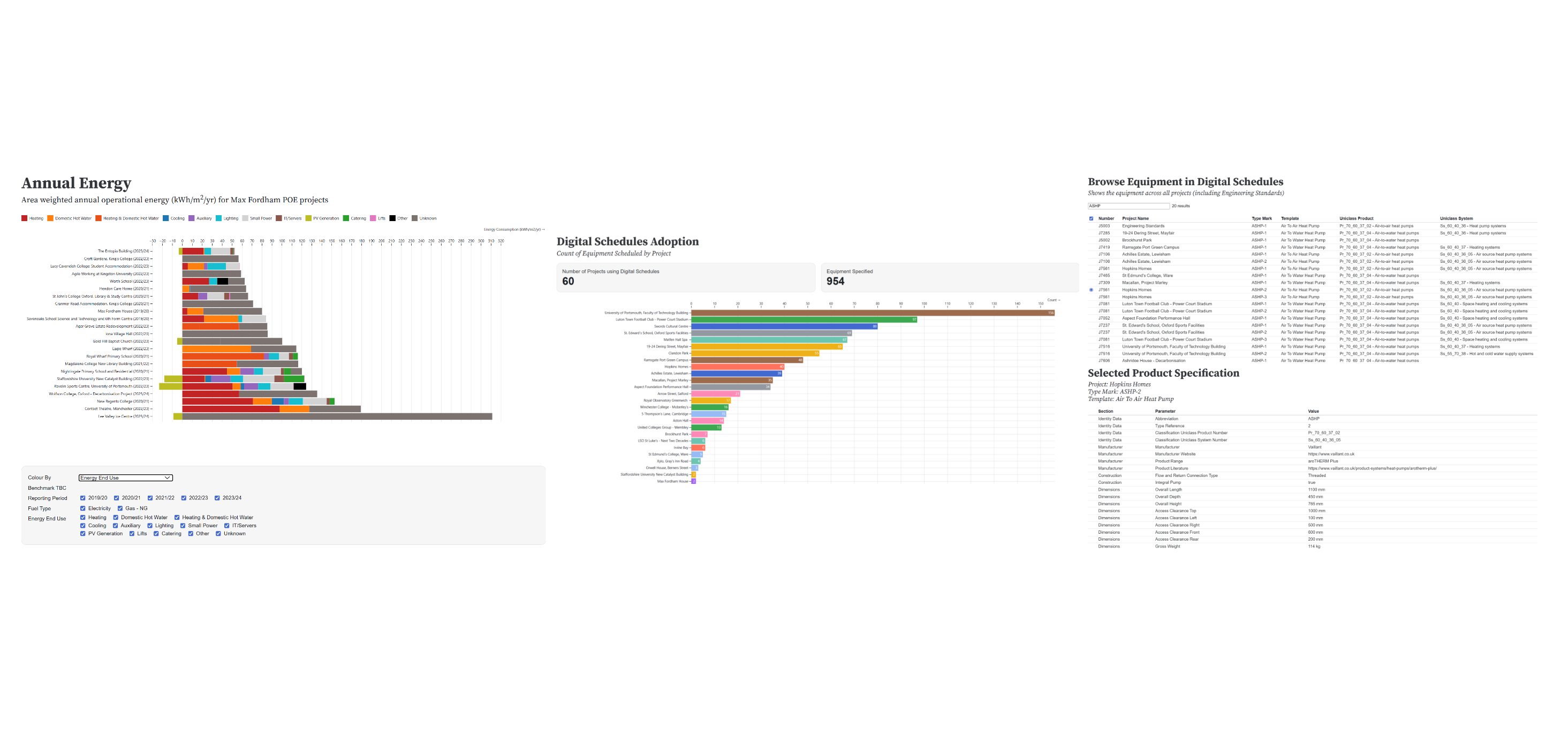
Observable Framework Dashboards
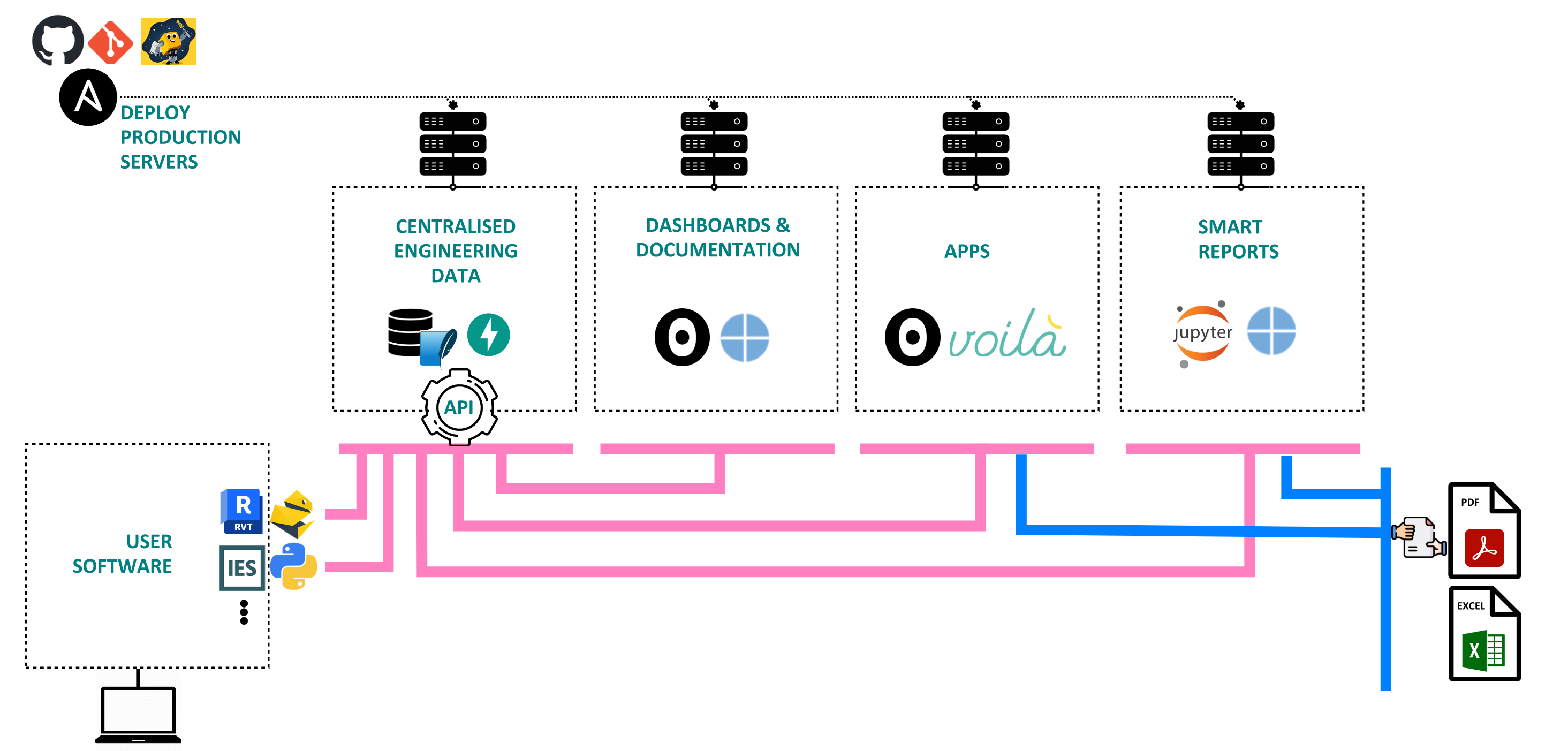
Growing Infrastructure over Time
The image below indicates how the platform is expected to grow to add additional apps, data and insights.